HostDesigner Tutorials
Making mengine input files
The mengine code is a command line executable that does molecular mechanics calculations. It is essentially the computational part of the old PCModel software, version 9. Because of this, mengine reads PCModel formatted input files. HostDesigner uses mengine to do molecular mechanics post-processing using either the MM3 or MMFF94 force fields. This topic is covered in detail in the HostDesigner User’s Manual, Section 6.
The procedure is as follows:
- HostDesigner writes a PCModel input file for the structure and writes a conpcm file telling the mengine what to do
- HostDesigner calls mengine
- mengine does the calculation and writes an output file containing structure and energy information
- HostDesigner reads the mengine output file.
In order for this post-processing procedure to work correctly, the user must assign force field atom types in the HostDesigner input fragment files.
PCModel input files are provided for a series of structures using either MM3 atom types and, where possible MMFF94 atom types, in order to assist with learning how to assign atom types (supporting information). These structures are shown in the graphics below.
The learning process:
- use PCModel to create the structure with a correct Lewis structure
- write a PCModel formatted file with either MM3 or MMFF94 atom types
- edit this file to check and/or correct the atom type assignments to make sure they are correct.
The learner can check their version against the provided reference PCModel files.
The user should refer to the HostDesigner User Manual as a guide for how to assign types.
In addition to atom typing, note that the MM3 model requires the correct marking of pi systems
whereas the MMFF94 model requires the correct specification of bond orders.
If you are working with metal complexes, then you will probably be using the MM3 model.
Note that one should never assume PCModel atom type assignments are correct.
They should always be checked and this is especially true for metal complexes.
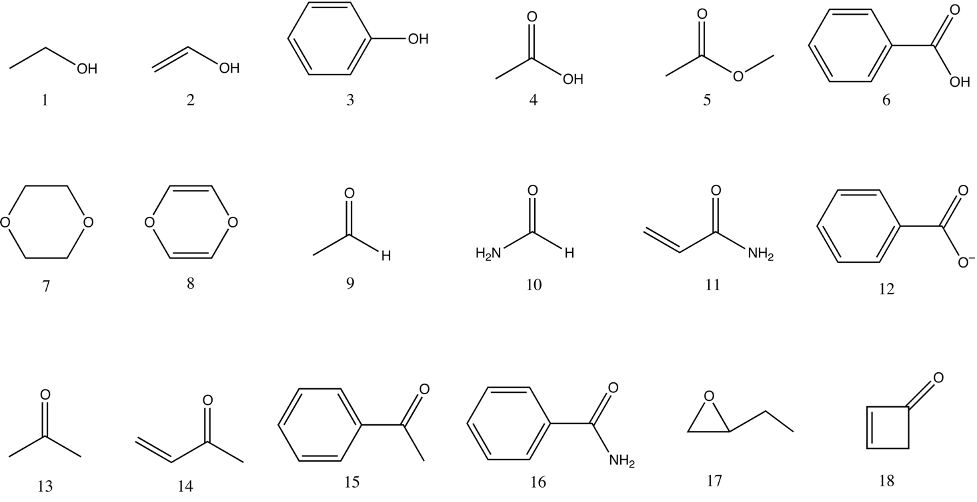
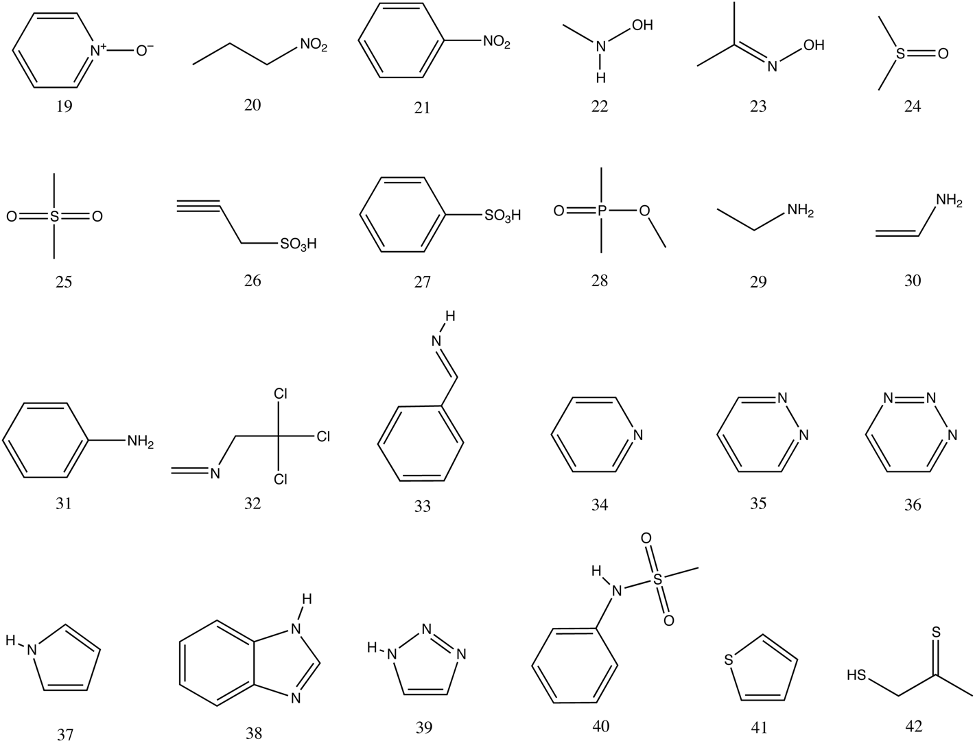
The Supporting Information contains a directory named atom_types, which contains PCModel input files for the 42 organic molecules shown above formatted using either MMFF94 or MM3 atom types. The file names include both the force field type and number of the structure. For example, the files for the first structure, ethanol, are named num1_mm3.pcm and num1_mmff.pcm. The training assignment is to use PCModel to create these molecules and save them as PCModel formatted files using both MMFF94 and MM3 atom types. The files produced by the trainee can be verified by comparison to the provided PCModel files.
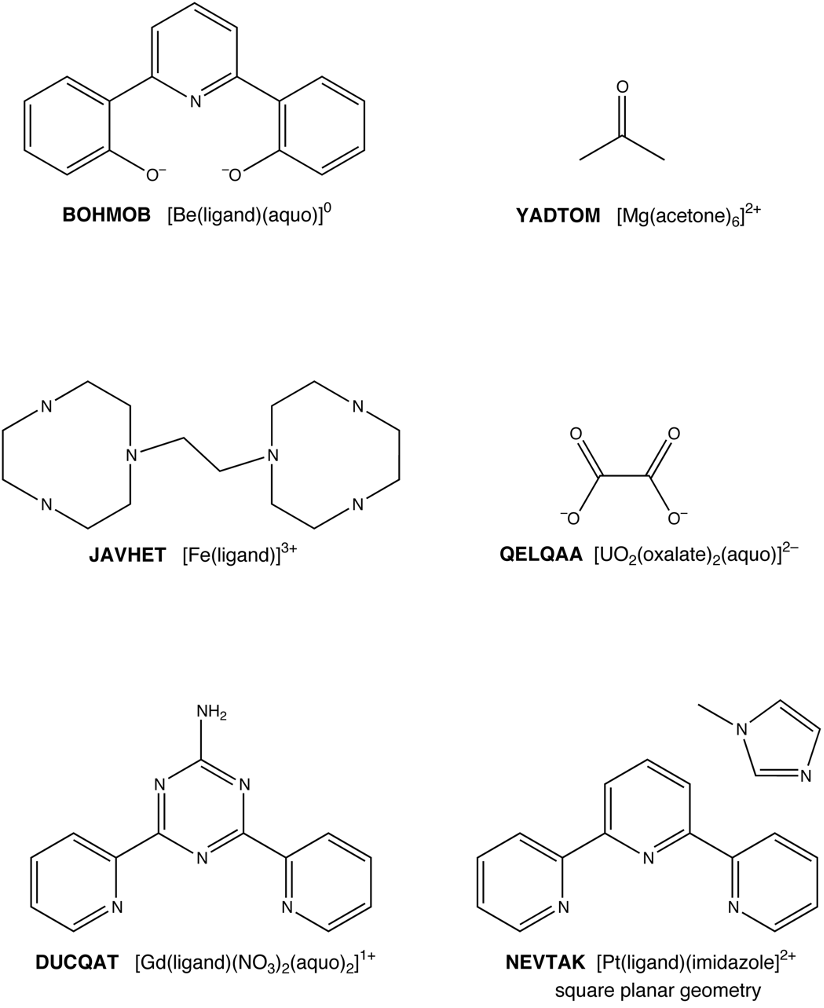
Atomic coordinates for the above metal complexes were taken from the Cambridge Structural Database. Supporting Information contains a directory named metal_complexes, which contains SDFmol formatted files and PCModel files with MM3 atom types for these complexes. The file names indicate the structure and the format. For example, the files for the first structure are named BOHMOB.mol and BOHMOB.pcm. The training assignment is to use the coordinates in the SDFmol file to create a PCModel input file with correct MM3 atom types. The result can be verified by comparison to the provided PCModel file.
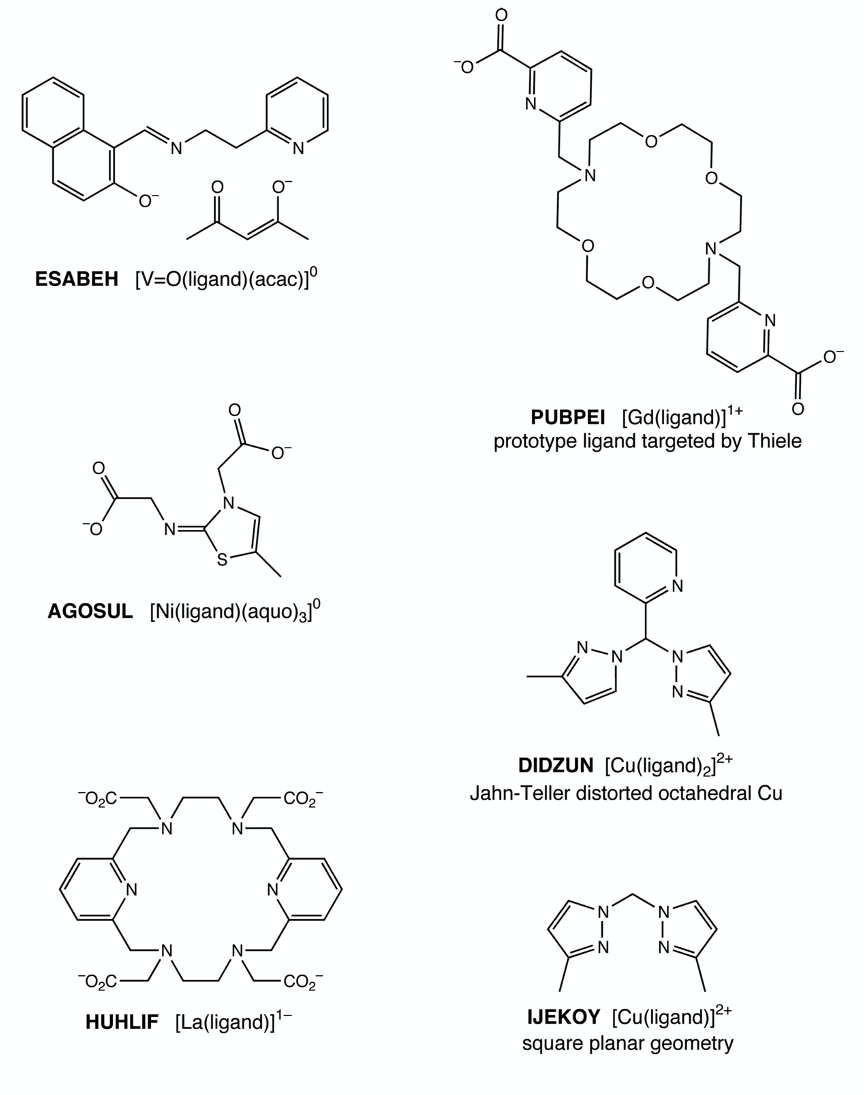
Continued from above, atomic coordinates for the above metal complexes were taken from the Cambridge Structural Database. Supporting Information contains a directory named metal_complexes, which contains SDFmol formatted files and PCModel files with MM3 atom types for these complexes. The assignment is to use the coordinates in the SDFmol file to create a PCModel input file with correct MM3 atom types. The training result can be verified by comparison to the provided PCModel file.